Abstract
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) causes cognitive impairment but it remains contested regarding which cognitive domains are most affected. Further, moderate-severe TBI is known to be deleterious, but studies of mild TBI (mTBI) show a greater mix of negative and positive findings. This study examines the longer-term cognitive effects of TBI severity and number of mTBIs in later life. We examined a subset (n = 15,764) of the PROTECT study, a cohort assessing risk factors for cognitive decline (ages between 50 and 90 years). Participants completed cognitive assessments annually for 4 years. Cognitive tests were grouped using a principal components analysis (PCA) into working memory, episodic memory, attention, processing speed, and executive function. Lifetime TBI severity and number were retrospectively recalled by participants using the Brain Injury Screening Questionnaire (BISQ). Linear mixed models (LMMs) examined the effect of severity of head injury (non-TBI head strike, mTBI, and moderate-severe TBI) and number of mTBI at baseline and over time. mTBI was considered as a continuous and categorical variable (groups: 0 mTBI, 1 mTBI, 2 mTBIs, 3 mTBIs, and 4+ mTBIs). Of the participants 5725 (36.3%) reported at least one mTBI and 510 (3.2%) at least one moderate-severe TBI, whereas 3711 (23.5%) had suffered at worst a non-TBI head strike and 5818 (32.9%) reported no head injuries. The participants had suffered their last reported head injury an average (standard deviation, SD) of 29.6 (20.0) years prior to the study. Regarding outcomes, there was no worsening in longitudinal cognitive trajectories over the study duration but at baseline there were significant cognitive deficits associated with TBI. At baseline, compared with those without head injury, individuals reporting at least one moderate-severe TBI had significantly poorer attention (B = −0.163, p< 0.001), executive scores (B = −0.151, p = 0.004), and processing speed (B = −0.075, p = 0.033). Those who had suffered at least a single mTBI also demonstrated significantly poorer attention scores at baseline compared with the no head injury group (B = −0.052, p = 0.001). Compared with those with no mTBI, those in the 3 mTBI group manifested poorer baseline executive function (B = −0.149, p = 0.025) and attention scores (B = −0.085, p = 0.015). At baseline, those who had suffered four or more mTBIs demonstrated poorer attention (B = −0.135, p < 0.001), processing speed (B = −0.072, p = 0.009), and working memory (B = −0.052, p = 0.036), compared with those reporting no mTBI. TBI is associated with fixed, dose, and severity-dependent cognitive deficits. The most sensitive cognitive domains are attention and executive function, with approximately double the effect compared with processing speed and working memory. Post-TBI cognitive rehabilitation should be targeted appropriately to domain-specific effects. Significant long-term cognitive deficits were associated with three or more lifetime mTBIs, a critical consideration when counseling individuals post-TBI about continuing high-risk activities.
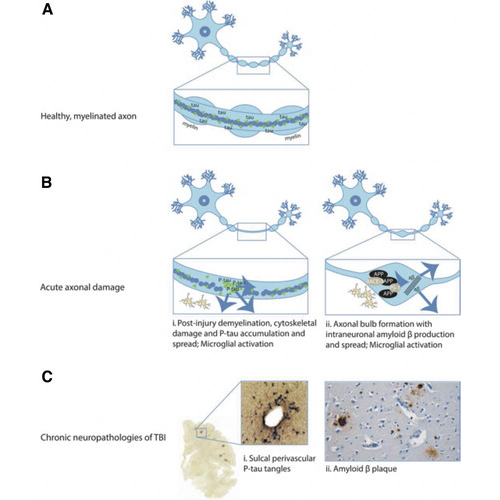
FIG. 1. Post traumatic brain injury (TBI) acute neuropathologies and chronic neurodegeneration. (A) Healthy, myelinated axon prior to TBI. (B) Acute axonal damage with demyelination of the axon (panels i and ii). (C) Chronic neuropathologies: (i) Tau pathology; (ii) amyloid B plaques. This figure is reprinted from Graham NSN, Sharp DJ. Understanding neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury: from mechanisms to clinical trials in dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2019;90(11):1221–1233; doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-317557 Crossref, Medline, Google Scholar
Conclusions
TBI in the chronic phase is associated with fixed, dose, and severity dependent cognitive deficits rather than more rapid rates of cognitive decline. The most sensitive cognitive domains are attention and executive function, with approximately double the effect compared with processing speed and working memory. Post-TBI cognitive rehabilitation should thus be targeted based on the domain specific effects. Finally, significant long-term cognitive deficits begin to be seen after only three lifetime mTBIs. This should be carefully considered when counseling individuals post-TBI about continuing high-risk activities.
